Monday 22 June 1942
 |
| "Fleet Air Arm planes starting out on an exercise carrying torpedoes." © IWM A 10683. |
Eastern Front: June 22, 1942, is the start of the second year in the Soviet Union, as General Halder notes in his war diary. Things look good for the Germans despite the failure to accomplish the end objectives of 1941. The grand offensive, Case Blau, that Adolf Hitlers sees as "clearing the table" in the East is ready and the Wehrmacht is reporting successes far and wide. Word of the Japanese defeat at Midway has not yet filtered through, and in any event, the Germans feel they can win the war on their own.
In Crimea, German troops continue cleaning out dwindling Soviet resistance on the north side of Severnaya Bay. On the southern and eastern fronts, the German 30th Corps remains stymied by fierce Soviet resistance backed by effective artillery fire on Sapun Ridge. Romanian 18th Infantry, 1st, and 4th Mountain Divisions continue slowly advancing along the Chernaya River toward Severnaya Bay. The Luftwaffe remains a dominant force, flying about 800 sorties and dropping about 700 tons of bombs every day.
General von Manstein, in command in Crimea, suddenly comes up with an innovative way to end the Sevastopol siege quickly. He asks General Halder for permission to parachute the captive Allied commander at Tobruk into Sevastopol to serve as a kind of object lesson on the futility of holding out. He predicts "a strong demoralizing effect." Halder does not even bother mentioning the crazy idea - which ignores practicality and the Geneva Convention - in his diary entry.
Luftwaffe General von Richthofen is ordered north to his new post helping out with Blau and given three days to get there. He wanted to remain for the ultimate victory, which now seems as far off as ever, and complains in his diary that he had originally been promised a full week to fly out. "It is a pity," he writes, "that one can never finish what one starts here in the east. After a while, it takes away all the pleasure."
Von Richthofen likes to dabble in ground operation strategy - all Luftwaffe generals are former army officers - and complains in his diary about Manstein's conservative approach (emphasis in original):
"I wish that everyone would just push a little more energetically. The view that advancing cautiously avoids losses is simply not correct, because small losses each day soon mount up the longer it takes."
Richthofen is a crony of Hitler and feels free to critique his peers freely in his diary. His assessments generally (but not always) appear quite reasonable.
Hitler finally returns to Fuhrer Headquarters in East Prussia after having been informed of the Reichel Affair on the 21st, and it is as though a dark raincloud has descended on the trapped generals. He summons Field Marshal von Bock, leader of Army Group South, to report on the situation. Halder reports "a great agitation conducted against the General Staff" about the loss of the plans for Blau to the Soviets. Nobody is quite sure what is going to happen to Blau, which today goes on four-days standby (so, projected to begin on 26 June). Halder notes that the pre-positioning of forces for Blau will take place today after dark.
 |
| Soviet Premier Joseph Stalin on the cover of Newsweek, 22 June 1942. |
On the Soviet side, Stalin has dismissed the Reichel Blau plans as disinformation, but not all of the Soviet generals are so sure. Colonel General Golikov, commanding the Bryansk Front, begins reinforcing his southern (left) flank. General Timoshenko further south, however, agrees with Stalin and believes that the papers were "fed to us deliberately in order to throw a veil over the true intentions of the German command." Golikov is taken aback by Timoshenko's head-in-the-sand approach and asks Stalin for a special commander to take over the sector in front of Voronezh. Stalin, however, still believes the German main effort will be toward Moscow to finish up the unfinished business of 1941 and turns him down flat. Since the Reichel papers indicated that the offensive would start on 22 June, at least so far the generals taking the papers seriously are starting to look foolish.
Operation Fridericus II, the remaining preliminary operation for Blau, jumps off in the morning. As with the recently concluded Operation Wilhelm, III Panzer Corps of Sixth Army carries the main load. It departs from the vicinity of Chuguyev heading toward Kupyansk, where it intends to turn south along the Oskol River. Further south, XXXXIV Corps of General Kleist's First Panzer Army crosses the Donets between Izyum and the mouth of the Oskol and heads north to close the pincer. It is still raining, as it has been for several days, and III Corps' panzers only make it halfway to Kupyansk. Halder notes that the operation:
made substantial initial ground gains, but later encountered stubborn resistance west of Kupyansk. Crossing of the Donets from the south has been executed without major difficulties.
An unexpected trend for the Germans is becoming apparent from these preliminary operations: the Soviets are not resisting. Rather than make defensive stands to stop or slow the German advances, the Red Army is simply giving ground. Nobody is quite sure what to make of this, and it is not entirely beneficial because the advancing troops are taking distressingly few prisoners.
Further north, things also are going well. Soviet Second Shock Army remains trapped west of the Volkhov River, though Halder notes that "Enemy tanks have penetrated into our 'bridge,' but... it is believed this will prevent the enemy from getting his forces out of the sac." He adds approvingly that "Starvation among the penned-up enemy is beginning to take its toll."
Battle of the Baltic: Soviet submarine Shch-317 torpedoes and sinks 2399-ton Swedish iron ore freighter Ada Gorthon west of Gotland (off Bläsinge, Öland). The ship sinks in less than a minute, and there are 14 deaths and 8 survivors.
Danish 81-ton freighter Ruth hits a mine and sinks in the Småland Sea off Sweden. The crew survives and they are later picked up by another freighter.
 |
| USS Meredith (DD-434) at sea off the Fiji Islands, 22 June 1942. Note the camouflage painting (Naval History and Heritage Command 80-G-13134). |
Battle of the Pacific: Port Moresby is now top of the agenda for both sides and can be considered the unofficial start of the battle for Port Moresby (which was the target of the failed Japanese invasion deterred by the Battle of the Coral Sea in May). Japanese forces of the Japanese 17th Army under Lieutenant General Harukichi Hyakutake in Papua, New Guinea begin the long 60-mile (100 km) trek over the mountains south toward Port Moresby. The terrain is rough and there are dense jungles along the way. Japanese forces use the Kokoda foot Track, which soars to 2190 meters (7,185 feet) at the peak of Mount Bellamy.
The Allies, in Operation Boston, send a garrison force from Port Moresby today to Milne Bay to develop an airfield. They also authorize another strip at Merauke, on the south coast of Dutch New Guinea, to protect the less-exposed western approaches. General Douglas MacArthur is the theater commander, while General Sir Thomas Blamey is the commander of Allied land forces for protection against Japanese overland attacks. Blamey is now in the process of deploying forces north to Kokoda.
Blamey's Allied Land Headquarters today orders Brigadier Basil Morris, commander of the 8th Military District of Australia, to deploy "Australian Infantry" to Kokoda (midway along the Trail) to block the Japanese advance (this takes a couple of days for Morris to undertake). The Allies also are in the process of building a vehicle track north toward Owers' Corner (38 miles, 61 km from Port Moresby), which generally is considered the southern terminus of the Kokoda Trail (completed late September).
USS Saratoga begins ferrying 18 Marine Dauntlesses of VMSB-231 and 25 Army Air Corps Curtiss P-40 Warhawks to Midway Island to replace aircraft lost during the Battle of Midway in early June. Admiral Fitch, the temporary commander of Task Force 11, is in command of the operation.
There is poor weather in the Aleutians, so some missions are canceled. A B-17 does manage a weather reconnaissance flight over the Japanese-held Kiska Island.
U.S. 44-foot tug Laura catches fire and sinks at Wood Island in Alaska.
European Air Operations: The Luftwaffe raids Southampton and neighboring Eastleigh during the early morning hours. Several homes are bombed and over a dozen people killed in the hardest raid in months.
 |
| Japanese troops land on Natuna Island, northwest Borneo, 22 June 1942. |
Battle of the Atlantic: Luftwaffe Junkers Ju 87 Stuka dive bombers attack shipping in the Kola Inlet. They sink minesweeper HMS Gossamer within eight minutes. There are 23 casualties. The Germans are preparing for a major effort to disrupt the Arctic convoys during the long summer days. The Soviets also lose two Sh-4 motor torpedo boats, No. 73 and No. 83.
U-159 (Kptlt. Helmut Friedrich Witte), on its second patrol out of Lorient, uses its deck gun to sink 9639-ton U.S. tanker E.J. Sadler southeast of Santo Domingo (west of Dominica). All 36 crew are rescued by destroyer USS Biddle.
U-202 (Kptlt. Hans-Heinz Linder), on its sixth patrol out of Brest, torpedoes and sinks 5864-ton Argentinian tanker Rio Tercero 120 nautical miles (220 km) southeast of NYC. There are five deaths and 37 survivors.
German patrol boat Sperrbrecher 14 Brockenheim hits a mine off Royan in the Bay of Biscay and is severely damaged, though it is towed back to port. Eventually, it is written off and scuttled as a block ship on 25 August.
British 242-ton fishing trawler (now ferry) Bromelia is being watched by a U-boat off Grimsby, North East Lincolnshire, Lincolnshire, England, when it suddenly hits a mine and explodes. There are 13 deaths.
 |
| Magazine ads are taking on a decidedly patriotic slant, such as this one from 22 June 1942 Time magazine p. 14. |
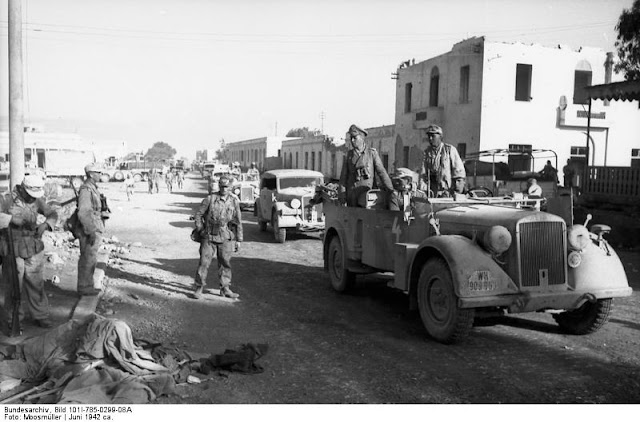
Battle of the Mediterranean: General Rommel's promotion has some immediate consequences. While nominally under the command of Italian generals at Commando Supremo, Rommel now feels even less bound by their decisions. During the day, a senior Italian staff officer shows up at his headquarters with General Bastico's orders to halt and consolidate gain, but Rommel disagrees. He already is planning a quick sweep east to disrupt the British before they can build strong defenses at Mersa Matruh.
Rommel has good reason to act quickly. German intelligence services inform him from intercepted communications that a U.S. military attaché in Cairo, Bonner Fellers, has told his superiors that, "If Rommel intends to take the Delta, now is the time." One of the reasons the Italians had such difficulties against the British before the arrival of the Afrika Korps was their conservative approach. So, the idea of stopping at Tobruk is anathema to Rommel.
He thus resorts to an appeal directly to Mussolini. Bypassing the chain of command normally would be prohibited, but the complicated international nature of the situation gives Rommel some flexibility. He writes a letter to Mussolini that is hand-delivered by the German attaché in Rome, Enno von Rintelen, in which he requests permission to continue advancing. He further requests that the projected invasion of Malta, Operation Herkules, be postponed so that he can keep his vital Luftwaffe support (which Field Marshal Kesselring already has begun withdrawing to Italy for the operation). He sums it up: "the goddess of success passes generals only once."
It is a clever decision, and it works. Mussolini already is arranging for a suitable white charger on which he can make his triumphal entry into Cairo. He immediately forwards the letter to Hitler.
The Germans no longer consider the British a factor in their plans (a similar tendency develops in Russia). Eighth Army is fleeing to Egypt, and General Ritchie has already abandoned any thought of making a stand at the border. Mersa Matruh, a fortified base to the northeast, seems much more defendable. Shattered British troops make the long, hot drive that they sardonically call the "Mersa Matruh Stakes."
 |
| Yakovlev Yak-7B prototype no.22-03 during trials in June 1942. |
Partisans: About 600 Italian police ("carabinieri") surround a home where three Albanian student communists (Branko Kadia, Perlat Rexhepi, and Jordan Misja) are holding out. They burn the building to the ground and execute the partisans. This becomes known as the Three Heroes of Shkodër (Shkrodra) and proclaimed as People's Heroes of Albania, with a patriotic song written about them.
A German anti-partisan operation, Operation Zenica-Zavidovići, concludes in the puppet state of Croatia. Fighting occurred mainly around Vlasenica to the east of Zenica. Most of the partisans have escaped to the southwest.
German Military: As a reward for victory at the Battle of Gazala and the capture of Tobruk, Hitler promotes Erwin Rommel to Generalfeldmarschall. This is not met with unanimous acclaim, as the Italian generals feel slighted after the very real contributions of Italian forces in the victory. Even Rommel is a bit indifferent, later confiding to his wife that he would have preferred being sent another division (throughout the campaign, he commands only three German divisions). Other German generals feel that the entire North African campaign is nothing but a sideshow and that Rommel is a reckless gambler - in their opinion, he should just hunker down and preserve his forces while the real work is done in Russia.
Rommel becomes famous in part for being Germany's youngest Field Marshal at the age of 50, though this is only partly true. Note that younger officers in the Luftwaffe, Generals Erhard Milch promoted on 19 July 1940 at age 48, and Wolfram von Richthofen on 16 February 1943 at age 47, become field marshals at younger ages. As a younger branch of the military, the Luftwaffe is well-known for having more room for advancement by younger men. This is also with the exception of Hermann Goering, chief of the Luftwaffe, promoted to field marshal at age 45 on 4 February1938 not for military feats but solely due to his position within the state hierarchy. Erwin Rommel, unlike the others, is famous for his overall generalship and ground victories rather than due to a position within the administrative apparatus.
US Military: Rear echelon troops of the First Marine Division set out from San Francisco aboard M/S John Erickson. They pass the time playing cards.
Holocaust: Adolf Eichmann sends an express letter to the Ministry of Foreign Affairs confirming a telephone call on the 20th in which he directed that Jewish resident of France, Belgium, and the Netherlands are to be sent to Auschwitz camp beginning "mid-July/the beginning of August." There are to be 40k from France, a similar number from the Netherlands, and 10k from Belgium. These are to be people "who are fit for labor, if they are not intermarried or hold the nationality of the British Empire, the USA, Mexico, enemy countries in Central or South America, or neutral or Allied countries." The "special trains" are to leave "every day."
In Plonsk, a Jewish Community in Warsaw Province, Poland, a 30-member communist group in the ghetto joins the Polish Workers' Party, or PPR. A party committee is established in the ghetto.
French Homefront: Prime Minister of France (aka Vice Premier) Pierre Laval, who is effectively running the French government as an ally of the Germans, makes a radio broadcast to the nation. He says in part:
I wish for a German victory, because, without it, Bolshevism tomorrow would settle everywhere.
Laval owes his return to the government in April to the German authorities, who view Premier Philippe Pétain as insufficiently supportive of the Axis. The way Laval frames his questionable reasoning as being more a stand against communism rather than simply blind support for the Reich becomes a common Axis theme and echoes common pre-war French political battles.
There is no question that Laval collaborates with the Reich, sometimes phrased more stringently as his being an "arch-collaborator."| However, Laval does now and then make a few small stands on behalf of France around this time that go unnoticed but make an impact on some people. For instance, in June 1942 he refuses a German demand for the forced deportation of 300,000 French workers as virtual slave labor in German war factories. Instead, he makes a counterproposal that one French POW be repatriated to France in exchange for every three French workers arriving in Germany. While a minimal gesture, it at least is something. Hitler accepts this, a rare concession to retain what support he has within the Vichy French government.
This is obviously not a major "victory for France" and does not excuse Laval's overall support of Germany during the war, but apparently does (or at least intends to) accomplish something positive for a very small sliver of Frenchmen that otherwise would not have happened. Laval's involvement in the Holocaust is murky, but he seems to go along with abhorrent German policies for the most part, though there are disputes about his participation and support.
American Homefront: Congress, in a Joint Resolution, formally adopts the words of the Pledge of Allegiance in the U.S. Flag Code. It was composed to celebrate the 400th anniversary of Christopher Columbus' arrival in the Americas. The author is Francis Bellamy, and it was originally published on 8 September 1892 in the children's magazine "The Youth's Companion." Reciting the Pledge in classrooms began spontaneously thereafter, and a surge of patriotism following the Pearl Harbor attack has made the Pledge popular among adults, too.
 |
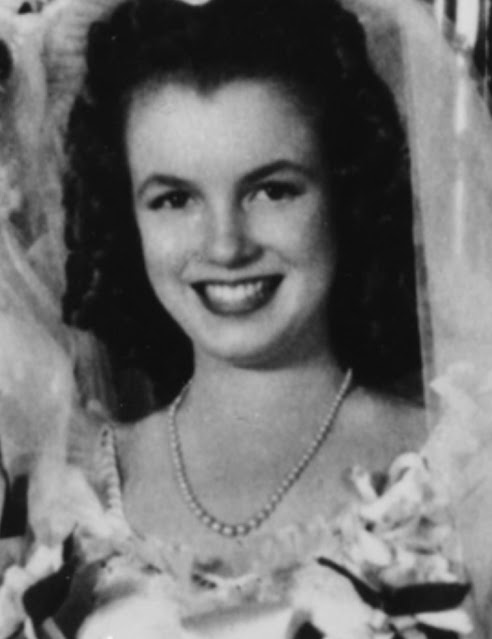
| Life magazine, 22 June 1942, "War Stamp Bride." |