Wednesday 10 June 1942
 |
| A still from a film taken by Gyles Mackrell, the tea planter who used elephants to save refugees in Burma. (Source: Cambridge University/PA). |
Eastern Front: Army Group South begins Operation Wilhelm, a short envelopment across the Donets River east of Kharkov, on 10 June 1942. This is not the opening of the main summer offensive, but just a preliminary attack to improve the launching pad for Case Blue. The offensive launches in rainy weather when III Panzer Corps captures two bridges across the Burluk River and turns upstream. The VIII Corps attacks north of Volchansk, taking three bridges on the Donets and bypassing Volchansk on the northeast.
While Army Group South commander Field Marshal Fedor von Bock calls the day's results "gratifying" and General Halder notes the attack has "started off well," the rain slows down the tanks and disrupts the tight timeline. Only the infantry keeps trudging along. The plan is for Sixth Army's VIII Corps to turn south once east of Volchansk to meet First Panzer Army's III Panzer Corps heading up from the south. Speed is of the essence, both because this is only one of a sequence of operations on the docket that all depend on each other's success and because the Germans want to trap the Soviet 28th Army west of the pincers before it can escape to the east.
Meanwhile, General Erich von Manstein's siege of Sevastopol continues to stumble. The Red Army forces in the port launch a counterattack today that is stopped with the heavy assistance of the Luftwaffe dropping anti-personnel bombs on them. No Axis progress at all is made in the south, where the 30th Corps is stopped by the 109th Rifle Division. Soviet defenses on the Sapun Ridge (Sapun-gora) prove highly resistant to Axis attacks. The German bright spot is in the north, where the 132d Infantry Division clears the Haccius Ridge, while the Soviets hold the Maxim Gorky fort only due a fierce defense put up by the Soviet 1st Battalion of the 241st Rifle Regiment.
At Fuhrer Headquarters, General Halder has a lot to say today, mostly coming across as a pundit who has no personal stake or influence on what he is describing, like a football announcer who has no impact on what he is saying:
Notwithstanding heavy enemy counterattacks, good progress at Sevastopol. It appears that the enemy has moved artillery and infantry from the southern sector to the threatened northern sector; the attack tomorrow, therefore, is to be launched with maximum surprise.
In other words, the initiative is no longer completely in German hands. In any event, the whole campaign in Crimea is a sideshow and is not expected to have a significant effect on the larger war.
The stress is getting to Luftwaffe commander General Wolfram von Richthofen. He becomes obsessed that there will be "friendly fire" incidents on Kriegsmarine ships and submarines. The commander of the German Black Sea Fleet (Admiral Schwarzes Meer) Vice-Admiral Friedrich Götting obligingly orders ships to sport prominent large Swastika flags as identification.
However, this good-faith gesture does not mollify Richtofen. Konteradmiral (Rear-Admiral) Robert Eyssen then sends Götting a message:
As it is impossible always to be informed if and when submarines and light forces of the German and Italian navies are in Crimean waters, Commanding General, 8th Air Corps [von Richthofen], has given orders prohibiting his planes from making any attacks whatsoever on any submarines or light forces, including Russian vessels in the entire Black Sea.
This is a strange situation, as there haven't been any friendly-fire incidents involving the ships. It leaves everyone but Richthofen shaking their heads. Götting is confused and exclaims:
There is no valid reason why these air attacks on submarines and light forces should be prohibited in the whole Black Sea area, as at present the German and Italian E-boats and submarines are only operating in the Crimean area.
Working behind von Richthofen's back, Götting then has Eyssen discreetly talk the matter over with the commander of Luftwaffe planes operating out to sea and not near Sevastopol where mistakes are likeliest, General Wolfgang von Wild. Eyssen and Von WIld privately agree that the prohibition makes no sense. Von Wild agrees to disobey this clear order and continue air attacks at sea (which the Kriegsmarine wants) outside of a small zone near Sevastopol.
This is a classic case of how these types of matters are handled in the Wehrmacht, technically insubordinate but just adapting to reality. It happens more and more as the war goes on, Wehrmacht fortunes deteriorate, and the German situation does not match up with Adolf Hitler's perception of reality.
 |
| Abkhaziya after the 10 June 1942 Luftwaffe attack. |
Luftwaffe Junkers Ju-88 bombers catch Soviet passenger/ cargo ship Abkhaziya at port in Sevastopol and sink it. Eight people lose their lives. The ship is raised after the war and broken up. The bombers also sink Soviet destroyer Svobodny (or Svobodney) at the south bay at Sevastopol. Svobodny has a crew of 271, but casualties are unknown.
Operation Kreml, a Wehrmacht deception campaign, shifts into high gear today. Army, corps, and division staffs begin holding meetings to discuss resuming the offensive toward Moscow by 1 August. The Luftwaffe also increases reconnaissance flights over Moscow and surrounding areas. Only the top people such as chiefs of staff and branch chiefs know the entire concept of an offensive toward Moscow is a complete sham and that the true orientation of the summer offensive is toward Stalingrad.
Operation Wilhelm, a Sixth Army operation near Izyum, begins today. It is a shallow pincer movement across the Burluk River intended to trap Soviet forces and set the stage for Case Blau. This minor local offensive is sometimes grandly styled as the beginning of the German summer offensive, but it is more a local, preliminary operation to secure a better launching pad for the main offensive. The operational plan is for VIII Corps in the north (south of Belgorod) to meet up with III Panzer Corps (east of Chuguyev/Kharkov) near Belyy Kolodez. A quick look at the map shows that the Germans have further to travel north and south than to the east, giving the Soviet forces plenty of time to escape the jaws of the pincer - which is exactly what happens.
Battle of the Pacific: The Imperial Japanese Navy today reports the results of the Battle of Midway to the military liaison conference in deliberately vague terms in order to not lose face after its staggering losses there. Admiral Chūichi Nagumo is not present and will not submit a detailed report until 15 June. The main Japanese goal now is to hide the results of the defeat as completely as possible, and elaborate steps are planned to do this once the fleet returns to Japan.
As part of this deception campaign, Tokyo radio today grandly announces the unopposed occupation of Attu and Kiska in the Aleutians as a "great victory." US Patrol Wing 4 is flying patrols over the two islands and now knows that they are occupied, but this silly broadcast could have given the US significant information under slightly different circumstances. In any event, this is an example of the blatant propaganda of World War II. Just to be fair, the Allies sometimes hide their own losses as long as possible, too (see, for example, the sinking of HMS Barham, sunk on 25 November 1941), but this takes disinformation that is not outright lying (what is broadcast is reasonably accurate, it's just the emphasis and omissions that make this pure deception) to another level.
Some practical steps based on the failed tactics of the battle are taken. From now on, returning planes will be refueled and re-armed on the flight deck rather than taken below to the hangars. All unused fuel lines are to be drained in order to reduce the chance of catastrophic fires. New carrier designs are prepared to incorporate only two flight deck elevators, which proved to be a severe vulnerability of the old designs. Enhanced training in damage control and firefighting is mandated, but this is commonly seen as "unheroic" and instituted more in theory than actual practice.
The Japanese reaction is understandable and does contain some good ideas, but the Japanese economy cannot replace the losses with nearly the capability of US industry. It is a classic case of "shutting the barn door after the horses have escaped." Training of replacement pilots must be accelerated, and this causes a drop in quality right when USAAF pilots are benefiting from their combat experience. The experienced crews, meanwhile, become overworked and dispirited, adding to the problems. The ships can and will be replaced, but the veteran pilots cannot.
The Japanese practice of mistreating prisoners that has permeated the war in the Pacific to date continues. While the Japanese attempt to cover their tracks carefully, they savagely execute the three U.S. Navy airmen taken prisoner during the battle in medieval style. Two are killed by tieing them to water-filled gasoline cans and then throwing them overboard.
Fifth Air Force raids Rabaul, bombing airfields and buildings.
In Sydney Harbour, Australian authorities use a crane to raise mini-submarine M-21 from the depths. Four Japanese crew members of the submarines are cremated and buried today with full naval honors at the Eastern Suburbs Crematorium.
Convoy OC 1, the first from Melbourne to Newcastle, begins today. This is part of tightened control over commercial sea traffic around Australia as a result of the Japanese attacks at Sydney Harbour and elsewhere.
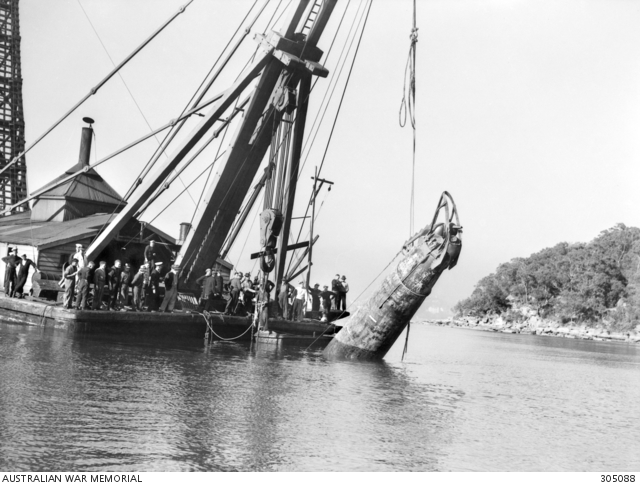 |
| A floating crane raising mini-submarine No. 21 in Sydney Harbour, 10 June 1942. Source: Australian War Memorial 30588. |
Battle of the Indian Ocean: Gyles Mackrell, a 53-year-old British tea exporter in the Indian provinces of Assam, uses about 20 elephants with Indian drivers to rescue at least 68 Burmese refugees (his own claim in his diary) or perhaps over 200 people (modern scholarship) fleeing the Japanese invaders across the treacherous Daphna River (swollen by monsoon rains) to India. Some are trapped on an island in the middle of the river that later washes away after the rescue. The elephants must walk more than 100 miles to even reach the river. The operation continues through the summer in spite of an order from British authorities to end it. Mackrell becomes known as "The Elephant Man" and is awarded the George Medal.
European Air Operations: The weather is 7/10th Cumulus clouds at 1500 feet (meters), so missions for the day are mostly scrubbed. The pilots spend the day watching combat films by Station Intelligence and the men find other ways to occupy themselves.
 |
| SS Surrey, sunk by U-68 on 10 June 1942, under way. |
Battle of the Atlantic: U-68 (KrvKpt. Karl-Friedrich Merten), on its fourth patrol out of Lorient, torpedoes and sinks three British freighters, 8581-ton Surrey, 5025-ton Ardenvohr, and 5882-ton Port Montreal, all northeast of the Panama Canal.
In the first action, Merten fires three torpedoes at Surrey, two of which hit, and one at Ardenvohr. Of the two ships, Ardenvohr sinks quicker, within about eight minutes. About 45 minutes after the first strikes on Ardenvohr, Merten fires a coup de grâce that fails to explode, and then a second that does. There is an unusual incident when Merten picks up a British seaman from Surrey found clinging to a buoy to rescue him, then finds a lifeboat and lets the man join his crewmates. There are a dozen dead and 55 survivors of Surrey and one dead and 70 survivors from Ardenvohr.
Five or six hours later, Merten spots Port Montreal about 178 miles north of Cristobal, Panama. The ship's crew also spots U-68, but it is too late. As it turns to run, the freighter is hit by a torpedo in the stern and this causes it to sink fast. Merten describes it in his personal war diary as a lucky hit. It may have been luckier than that for the ship's crew, because Port Montreal is carrying 7500 tons of ammunition that could have created quite an explosion if the ship had been hit broadside. There are two dead and 86 survivors, who are picked up on 16 June by Colombian schooner Hiloa.
U-94 (Oblt. Otto Ites), on its ninth patrol out of St. Nazaire, also makes a convoy attack and hits multiple ships, this time southeast of Cape Farewell. All three torpedoes strike, though it is unclear which ship got hit twice. In any event, both ships sink. The victims are two British freighters, 4855-ton Ramsay and 6147-ton Empire Clough. There are eight survivors and 40 dead on Ramsay and five dead and 44 survivors on Empire Clough. Survivors of the ships are picked up by Portuguese trawler Argus, escort destroyer HMS Vervain (K 190), and the escort destroyer HMS Dianthus (K 95).
 |
| "Original wartime caption: The British swimming club at Beirut is a popular rendezvous for both Free French and British forces." 10 June 1942. © IWM E 13191. |
U-129 (Kptlt. Hans-Ludwig Witt), on its fifth patrol out of Lorient, torpedoes and sinks 4362-ton Norwegian freighter L.A. Christensen well east of Miami while en route from Durban to Philadelphia. The ship sinks within 12 minutes, but the crew has enough time to launch the lifeboats and all 31 crewmen survive. They are picked up after 12 hours by Norwegian freighter Bill. This is the first victory in a very successful cruise by U-129 during which it sinks over 40,000 tons of shipping.
U-107 (Kptlt. Harald Gelhaus) is usually credited with the sinking of 2606-ton US freighter Merrimack about 60 miles from Cozumel Island, Mexico. I have my doubts, because my records show that U-107 is in between patrols on 10 June 1942, but it's possible. More likely in my view is that an unidentified Italian submarine did the deed. Anyway, most of the crew abandons ship in one overcrowded lifeboat (the other is destroyed by the explosion). Unfortunately, all in the boat perish when it is sucked into the freighter's still-spinning propeller. Other men, including the master, simply jump overboard and make it to rafts. This proves to be the more successful strategy. Overall, 31 crewmen survive and 43 perish, with the lucky men in the water spotted by a PBY Catalina and picked up by USS Borie (DD 215).
Speaking of Italian submarines, Leonardo da Vinci uses its deck gun and a torpedo to sink 5483-ton Dutch freighter Alioth the ship is en route from Birkenhead to Capetown. I can't find a more precise location, but Italian submarines tend to operate south of the Mediterranean and often in the general vicinity of Sierra Leone. I'm guessing this was near Freetown. Everybody survives. This sinking is sometimes listed as occurring on 11 June 1942. Italian submarine captain records tend to be much spottier than their more precise and detailed Kriegsmarine counterparts.
Soviet submarine D-3 ("Krasnovgardeyets") mysteriously sinks with all hands in Varangerfjord, Norway (at the most northeastern portion of Norway, north of Finland). One theory is that the submarine hit a mine.
Norwegian 6049-ton freighter Haugarland hits a mine and sinks in the North Sea off Terschelling, Netherlands. The ship takes a day to sink, so this is usually listed as occurring on 11 June 1942.
Royal Navy 96-ton drifter Groundswell, being used as minesweeper under the name Trusty Star, either hits a mine and sinks off Malta or is sunk there in an air raid. Either way, casualties are unknown.
 |
| "Universal carriers and infantry of 10th Battalion, Royal Berkshire Regiment advance 'under fire' during training near Sudbury in Suffolk, 10 June 1942." © IWM H 20536. |
Battle of the Mediterranean: Fierce air battles continue above the fortress of Bir Hakeim, with the RAF's Desert Air Force flying more slightly more sorties than the Axis but also losing more planes. The Free French at Bir Hakeim begin retreating in small groups from Bir Hakeim during the early morning hours but continue to maintain the defense of the fortress throughout the day. The French are almost out of ammunition but manage to hold their lines against a determined Afrika Korps attack in the north. The Messmer and Lamaze units counterattack to restore the line, supported by Bren Gun Carriers, but expend their last mortar rounds during the day. The French are reduced to searching the corpses of their comrades for rifle ammunition.
After dark, the French send sappers to clear mines from the western side of the fortress to open an escape route and General Kœnig drives out around 20:30 in a Ford ambulance driven by Susan Travers, the only (unofficial at this time) female member of the French Foreign Legion who is assigned tot he medical detail. Kœnig and Travers barely make it out in their bullet-ridden vehicle. A small force of the Foreign Legion remains behind at the fort to disguise the retreat.
The Axis troops quickly get wind of this retreat and send up a flare, showing the column of French vehicles heading west and south. The 90th Light Division tries to block the road, but Kœnig orders the column to blast through, which it does during a wild mêlée in the dark. British troops of the 550 Company Royal Army Service Corps (RASC), escorted by the 2nd King's Royal Rifle Corps (KRRC) and the 2nd Rifle Brigade, assist the breakout from the south. Despite suffering many casualties, including the day's hero, Lamaze, Capitaine Charles Bricogne, and Lieutenant Dewey, most of the French manage to escape to British lines at Bir el Gubi. Foreign Legion commander Amilakhvari performs the sacrificial duty of remaining in command of a skeleton force holding out in the fortress.
Everyone with a map can see that Tobruk is in danger, so the British ramp up their supply activities to the port. That leads to a great deal of activity along the convoy route and some Allied losses today.
U-559 (Kptlt. Hans Heidtmann), on its eighth patrol out of Salamis, attacks two ships in Convoy AT-49 heading to Tobruk. At 04:56, Heidtmann attacks the convoy by firing three torpedoes and reports hits on a tanker and freighter. The former is 4681-ton Norwegian tanker Athene, which blazes for a full day before sinking due to its cargo of 600 tons of aviation fuel. There are 14 dead and 17 survivors. The latter ship is 5917-ton British oiler Brambleleaf, whose crew abandons ship and are picked up by RHS Vasilissa Olga (D 15) (seven dead and 53 survivors). Brambleleaf is towed to Alexandria, where it is used as an oil hulk until it suddenly sinks on 15 September 1944.
U-81 (Kptlt. Friedrich Guggenberger), on its seventh patrol out of Salamis, torpedoes and sinks 2073-ton British freighter Havre in the same Tobruk convoy. There are 20 dead and 30 survivors, who are picked up by British armed trawler HMS Parktown.
Operation Harpoon, another complicated convoy operation with British ships sailing from both ends of the Mediterranean to resupply Malta and British forces in Egypt, begins today. It is under the command of Admiral Vian on the Alexandria side and Admiral Curteis on the Gibraltar side. Some freighter sail independently, depending on the convoys to distract the Axis defenses.
 |
| HMS Trusty Star, sunk 10 June 1942, on the seafloor. Source: Gration, Dave, Heritage Malta. |
Partisans: German and Ustaše authorities begin the Kozara Offensive, an attack against partisan forces around the mountain of Kozara in the former Yugoslavia. The Germans supply 15,000 soldiers and the Independent State of Croatia over 20,000. The Hungarians supply five monitor ships.
As with most anti-partisan operations, the Kozara Offensive suffers from the difficulty of telling actual partisans from ordinary civilians. The mountainous, forested terrain also gives the defenders ample opportunities to take potshots at the advancing Axis forces from concealment. This leads to several times as many casualties on the Axis side. The partisan forces concentrate their units in the city of Široka Luka, with a major formation led by Josip Broz Tito. The Axis troops take many captives, but it is difficult to tell the partisans and civilians apart and the Germans wind up shipping them from Kozara to Sajmište concentration camp.
Applied Science: The US Navy establishes Project Sail at NAS Quonset Point, Rhode Island. This program will perform airborne testing of Magnetic Anomaly Detection (MAD) and other advanced projects such as 10 cm radar.
US/Soviet Relations: Soviet Foreign Minister Molotov is in Washington, D.C., as the Allies attempt to iron over some differences in strategy. Stalin wanted an invasion of northwestern Europe in 1941, and Molotov now presses home the urgent need for one in 1942. However, President Franklin Roosevelt fobs him off with vague phrases and unenforceable "wishes" and "hopes" that it might happen. In fact, Roosevelt knows that the Joint Chiefs of Staff have no plans whatsoever for an invasion of France in 1942. Instead, they are beginning to look at North Africa as the place to start. As a sign of good faith and comity among allies despite their other disagreements, Secretary of State Cordell Hull and Foreign Minister Maxim Litvinov jointly sign a new Lend-Lease Agreement.
US Military: The second contingent of the 1st Armored Division arrives at Belfast on passenger ship Oriente. The division still does not have its full complement of tanks. Other soldiers from the 141st Armored Signals Company arrive on Dutchess of York, and the 47th Armored Medical Battalion arrives on SS North King.
German Military: Bernhard Woldenga, Geschwaderkommodore of JG 27, is promoted to a staff posting. The Luftwaffe often does this with officer pilots who are considered too valuable to lose in combat (Adolf Galland is the best example of this) or too vulnerable to keep flying for some reason. Woldenga is ill, so this case is probably the latter reason. Replacing him is Major Eduard Neumann replaces Woldenga, Hptm. Gerhard Homuth replaces Neumann as Gruppenkommandeur of I./JG 27, and Oblt. Hans-Joachim Marseilles replaces Homuth as Staffelkapitaen of 3./JG 27. This is quite a change of fate for Marseilles, who began his Luftwaffe career as a virtual outcast due to his unorthodox ways.
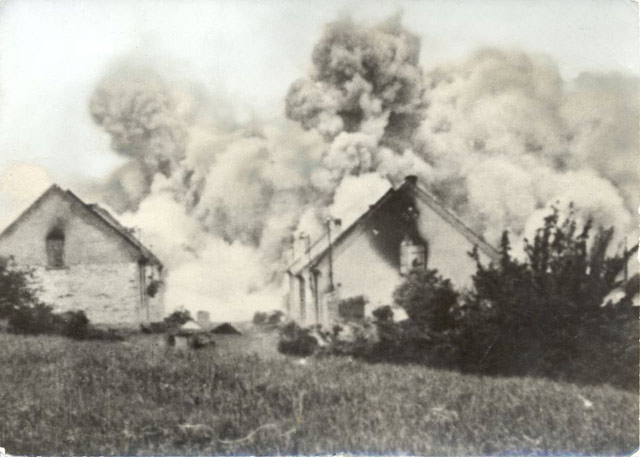 |
| German occupation authorities blow up the town of Lidice, 10 June 1942. Source: Lidice Memorial. |
German Homefront: Having decided for spurious reasons that the Czech village of Lidice (20 km west of Prague) harbored the assassins of Reinhard Heydrich, the local authorities destroy the town. The operation is savage and permanent. The town has 503 residents and all who are found are disposed of in some fashion.
The Germans arrive right after midnight and herd all the villagers into the main square. The Germans shoot all 173-199 men aged 14 to 84 that they find at a local farmhouse and send 195 women to Ravensbrück concentration camp (four pregnant women are forced to have abortions and then are sent to the camp). Women who refuse to leave their husbands are shot with them. The women are not told what happened to their husbands. The Germans make a point of tracking down village residents who happen to be out of town that day and kill them, too. The authorities then destroy every building and even dig up the town cemetery.
The men are stood in long rows and there they fall. The photos show them laid out in eerily precise order in rows outside the farmhouse awaiting burial. Inmates at local concentration camp Terezin are made to dig mass graves for the victims.
Of the 95 children in Lidice, 81 are sent to Chelmno extermination camp in Łódź, Poland, to die, while eight or nine who have Germanic features are adopted by German families after first being brought to Puschkau, Poland, to learn German ways. In all, only 17 children survive the war. One of them, Václav Zelenka, later becomes mayor of the rebuilt town of Lidice.
The Germans carefully the results of the operation. They show it proudly widely to illustrate to anyone thinking of challenging their rule what might happen to their homes, too. It becomes worldwide news and helps harden hearts against the Third Reich.
The Germans also plan to destroy the smaller Czech village of Ležáky, which actually does have a connection to the Allies as evidenced by a forbidden radio transmitter belonging to Operation Silver A, a three-man Czech squad trained and inserted by the British SOE and RAF that is separate from, but assisted, Operation Anthropoid (the mission to assassinate Heydrich). All adults in Ležáky are to be killed and the leader of Silver A, Alfréd Bartoš, commits suicide.
The two agents who assassinated Heydrich, Jozef Gabčík, Jan Kubiš, remain at large despite a massive German manhunt. They are being shuttled between safe houses provided by the Jindra group. Frustrated, the Germans have adopted a carrot-and-stick approach to this problem, offering a huge reward and threatening further savage reprisals if the men are not betrayed. This is being heard with receptive ears.
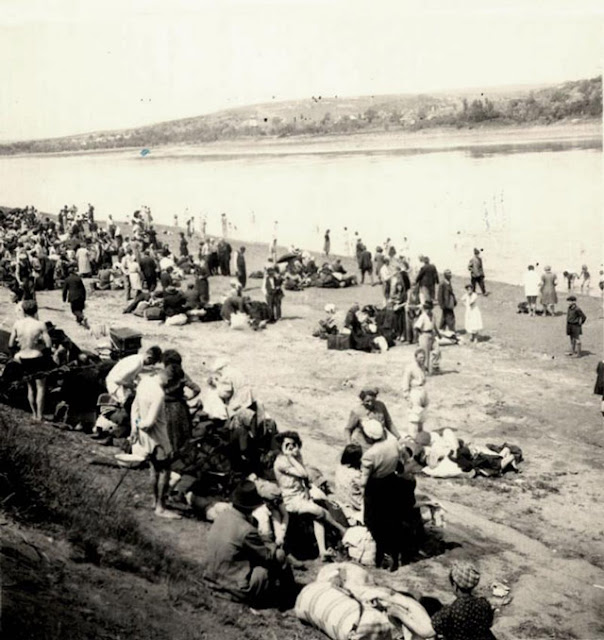 |
| Jewish inhabitants are assembled on the western bank of the Dneister River. They await deportation by Romanian authorities, who control the area based on ancient claims, to the Transnistria region across the river. Yad Vashem. |
British Homefront: As announced in the King's Birthday Honours on 5 June 1942, economist John Maynard Keynes receives a hereditary peerage. He acquires the title "Baron Keynes, of Tilton, in the County of Sussex," and now is entitled to sit in the House of Lords on the Liberal Party benches.
American Homefront: Congress gives final approval to the "Big Inch" pipeline. This will transport crude oil from its production site in Texas to the northeast. This has become necessary due to U-boat successes against tankers along the east coast of the United States.
Ernest Preston Manning is born in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. He becomes a member of Parliament for Calgary Southwest in 1993 under the Reform Party and leads the party until it is abolished in 2000. He then switches to the Canadian Alliance from 2000 to 2003 and has been in the Conservative Party since 2003.
 |
| "Original wartime caption: A British and Free French soldier set out in search of another diversion from the British Swimming Club." 10 June 1942. © IWM E 13193. |
2021